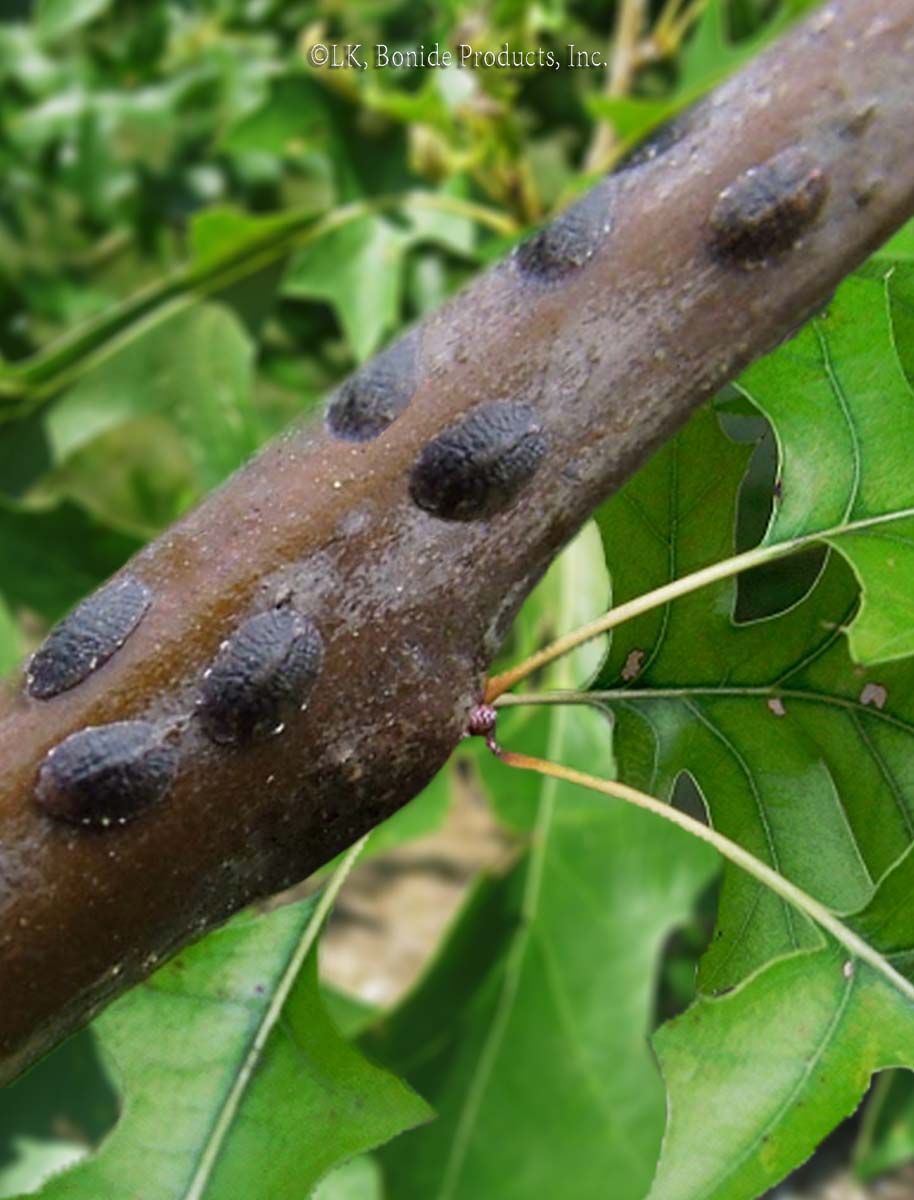
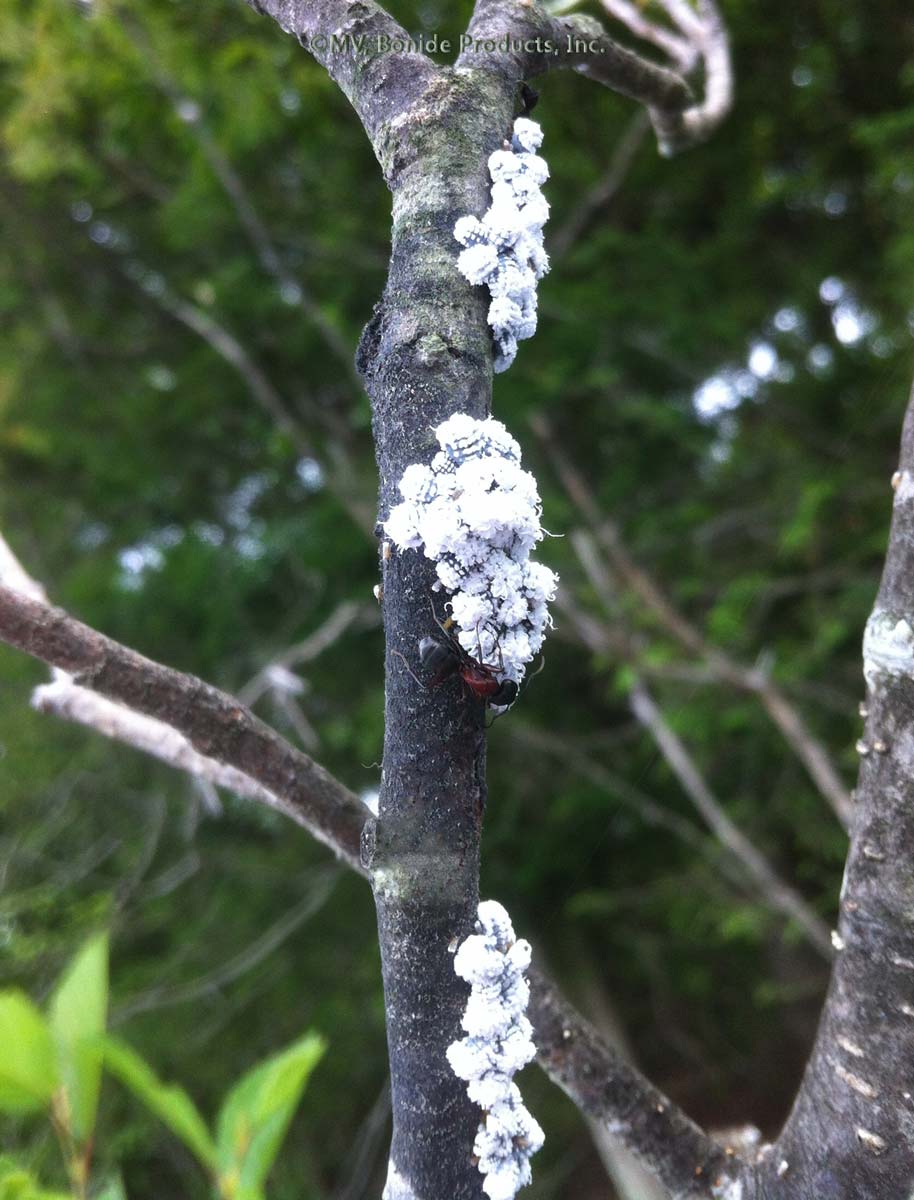
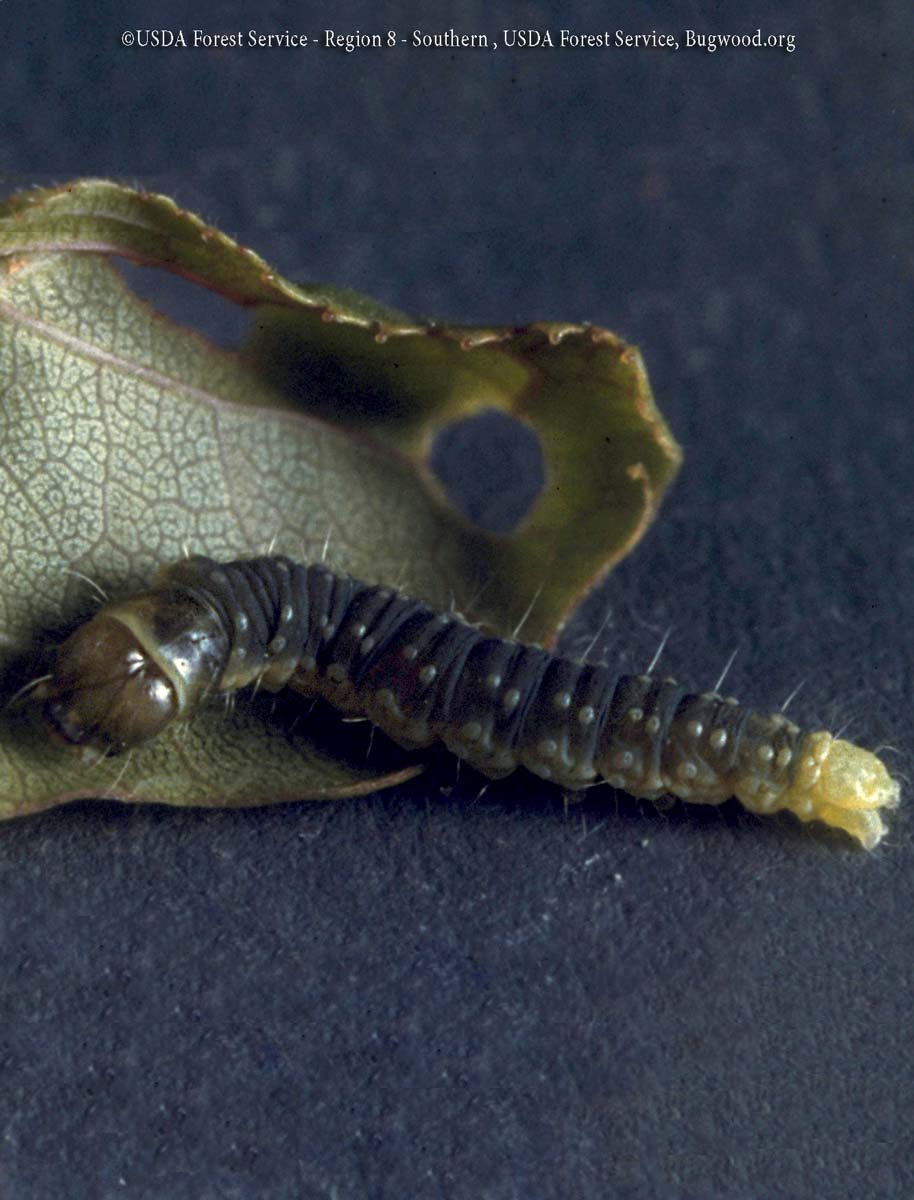
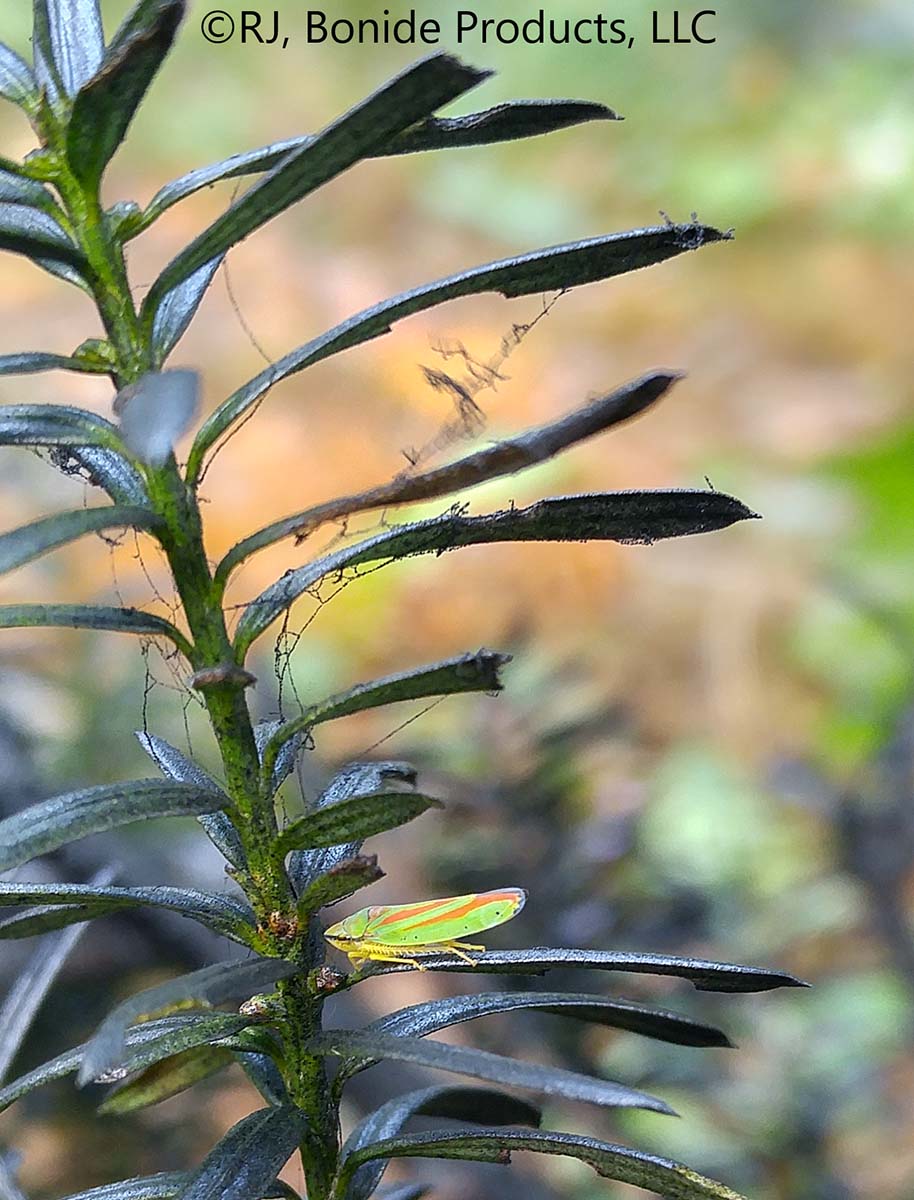
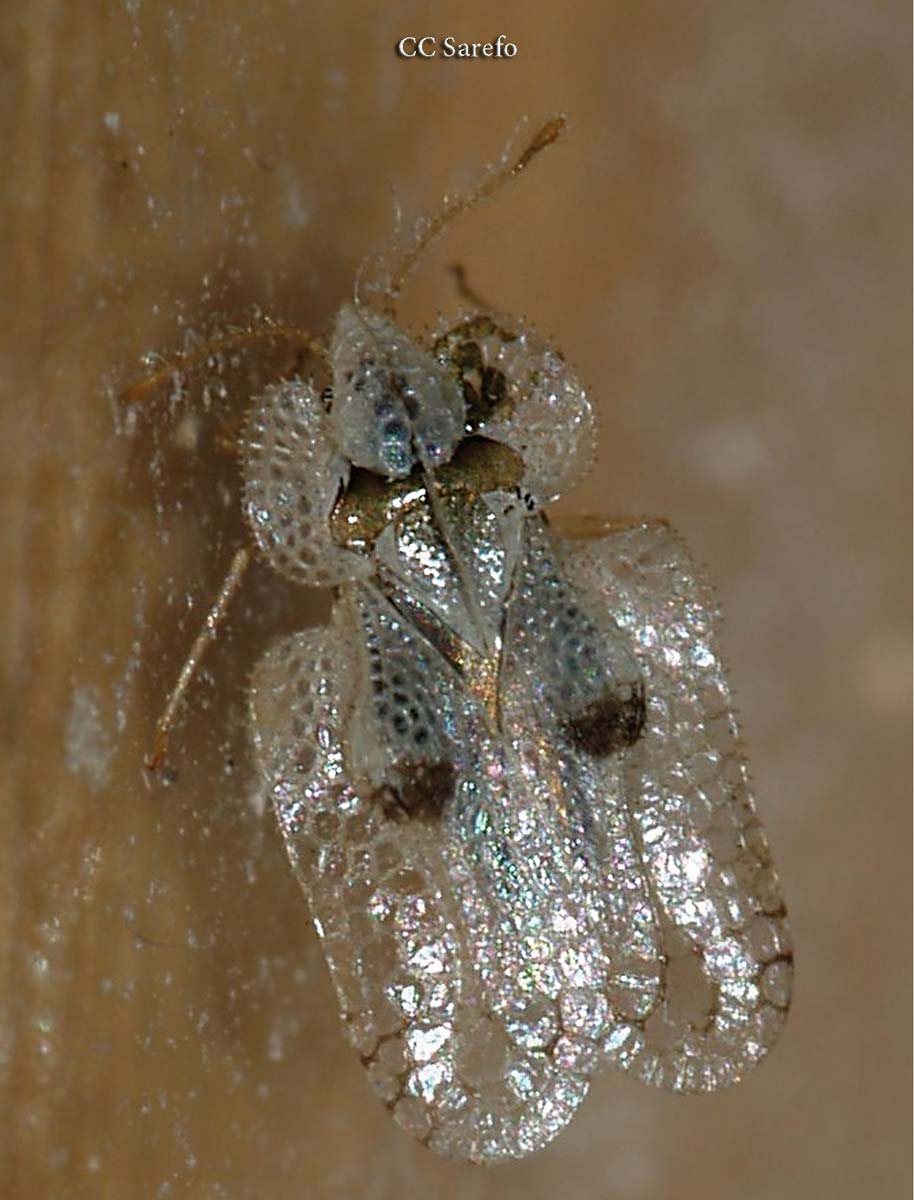
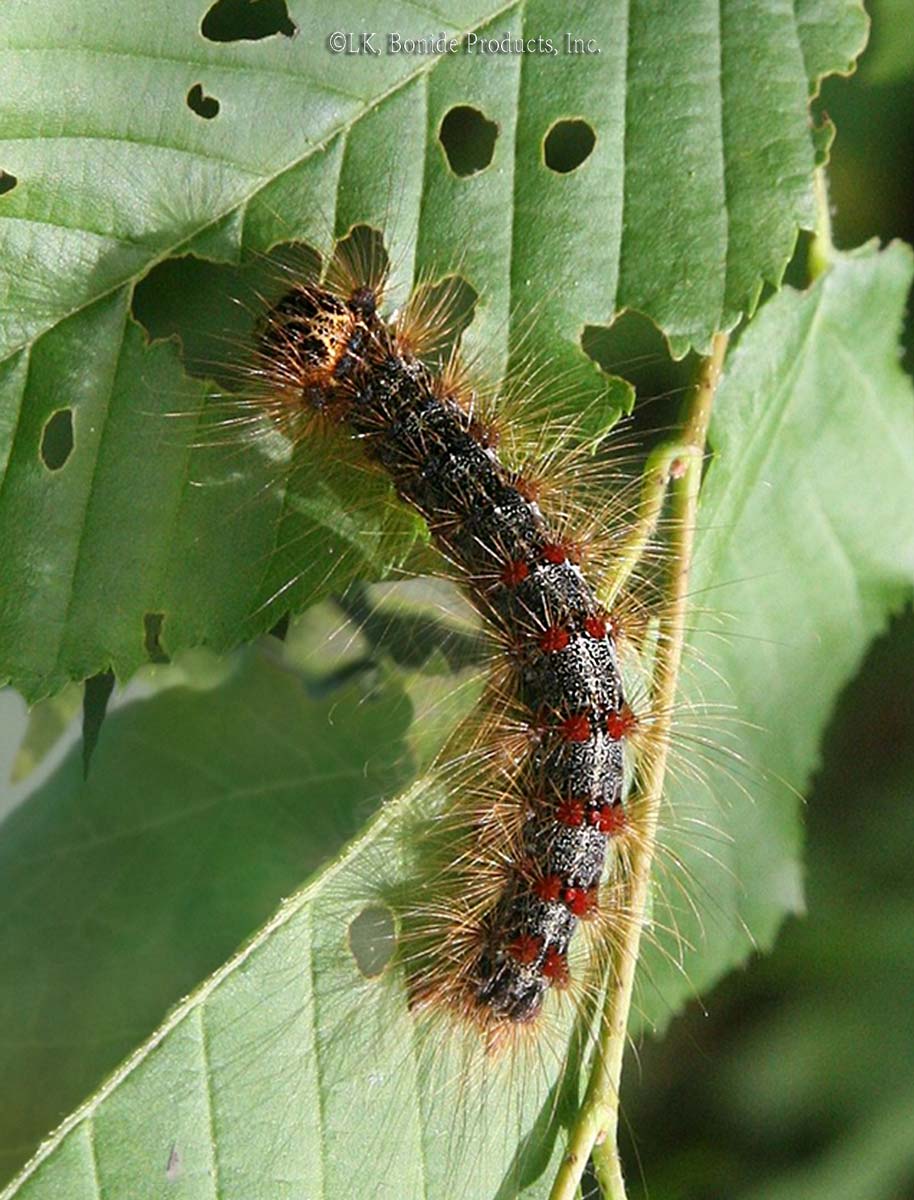
Scale Insects
Varying in size, shape, and color, the many species of these aphid cousins look like bumps on bark, leaves, and fruit. All are equipped with an insecticide-resistant coat, a leathery or waxy material in the case of soft scales, a sturdier covering for armored scales. Young scales (called crawlers) move around the plant, but they … Read more